Rows (horizontal lines) of the Periodic Table are called periods; the elements in a period are NOT similar to each other.
Columns on the Periodic Table are called Families or Groups. The elements in a family ARE similar to each other.
You can see the color coded important areas of the Periodic Table at ptable.com.
This Periodic Table diagram shows where to find four of the element families:
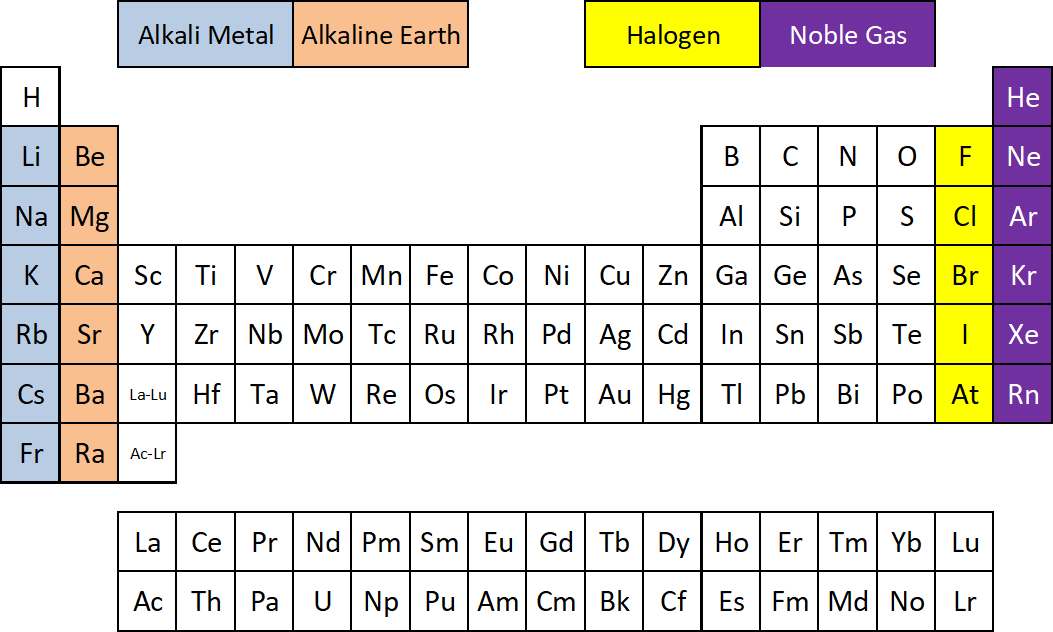
Alkali Metals
•first column on the left of Periodic Table, also known as Group 1.
•very reactive metals – reacts with air and water
•”alkali” because they react to form a base (alkaline = base) in water
•shiny, conductive, very soft/malleable
•includes Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs
Alkaline Earths
- The second column from the right, also known as Group 2.
- Includes Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra
- Soft metals with low density and low melting and boiling points (low for metals, at least)
- Alkaline means basic (opposite of acidic), and these metals form basic solutions when mixed with water
- The “earths” part of the name relates to the fact that these elements are usually found as compounds (combined with other elements) that are not soluble in water.
Halogens
•The second to last column of the table, also known as Group 17
•Very reactive nonmetal family; includes F, Cl, Br, I
•Reacts with many different chemicals; reacts with most metals, most nonmetals, many organic compounds
Noble Gases
•last column of the table, also known as Group 18
•includes He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn
•colorless, odorless, tasteless gases
•very stable / unreactive; very difficult to get them to form compounds with anything